Why is it worth trusting us?
DR TUROWSKI Hair Restoration Clinic jest jednym z najbardziej doświadczonych ośrodków robotycznych przeszczepów włosów na świecie. Zespół pod kierownictwem dr Turowskiego przeprowadził pierwszą w Polsce i Europie Środkowo–Wschodniej operację przeszczepu włosów metodą FUE – ARTAS i obecnie wykonuje ponad 400 zabiegów rocznie.
Doświadczenie Polsko-amerykanski zespół transplantacji pod kierownictwem dr Turowskiego
30 milionów przeszczepionych mieszków włosowych
technologia Jedyna klinika w Polsce dysponująca dwoma robotami Artas 9 i Artas iX
Raty 0% Korzystne warunki współpracy
You have a problem with baldness?

Zobacz metamorfozę
Piotra Świerczewskiego
Utytułowany sportowiec, prawdziwy „twardziel” na boisku i entuzjasta zdrowego stylu życia, podobnie jak wielu mężczyzn po 30-tce, od dłuższego czasu bezskutecznie walczył z łysieniem. W końcu zdecydował się na zabieg przeszczepu włosów w DR TUROWSKI Hair Restoration Clinic.
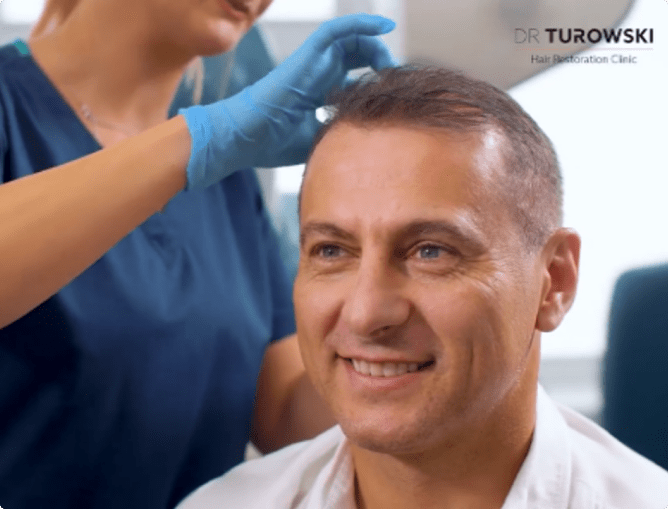
Jak wygląda proces?
konsultacja ze specjalistą
zabieg przeszczepu włosów
rekonwalescencja
uzyskany efekt
Poznaj opinie naszych Pacjentów
To najlepsza rekomendacja naszej kliniki! Sprawdź, dlaczego jesteśmy liderem w dziedzinie przeszczepu włosów.
Nasze zabiegi przeprowadzamy w naszych klinikach w Polsce w Warszawie i Katowicach





















 ZADZWOŃ
ZADZWOŃ